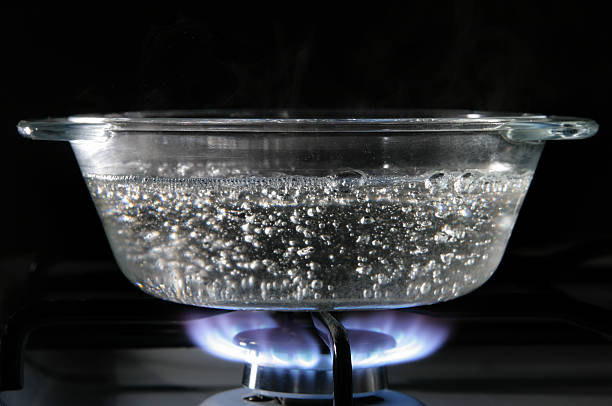
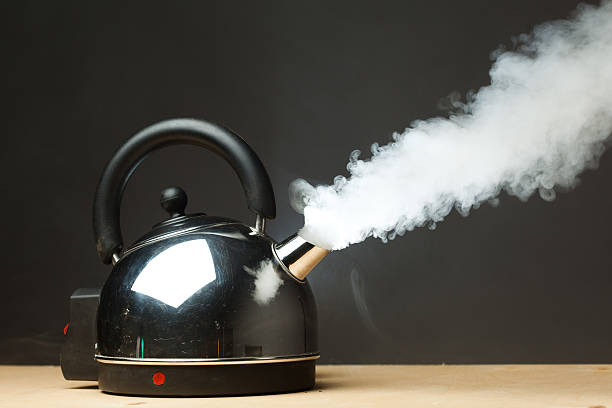
Since the water vapors retain the same molecular structure as the liquid water after boiling, boiling of water is a physical change rather than a chemical change. Molecules do not undergo any chemical change when water boils.
The phenomenon of boiling water is crucial to comprehending the characteristics of water.
This article answers the question ” Is boiling water a chemical transformation?”.
Table of Contents
What is the Boiling Point of Water?
Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius, or 212 degrees Fahrenheit (sea level), at one atmosphere of pressure. However, the value fluctuates. The atmospheric pressure, which changes with elevation, has an impact on the boiling point of water. As you ascend, the temperature at which water boils drops (e.g., ascending a mountain), and it boils at a higher temperature as atmospheric pressure rises (coming back down to sea level or going below it).
Purity also has an impact on water’s boiling point. Water that contains impurities, such as salted water, boils at a higher temperature than pure water. This phenomenon is known as “boiling point elevation,” and it is one of the water’s colligative properties.
Is the Boiling of Water a Chemical Change?
Not a chemical change occurs when water boils.
A physical change is boiling. An alteration in a substance’s physical characteristics is considered a physical change. A physical change can typically be undone. Such a change results in the formation of no new substance.
Water boiling, ice melting, water freezing, sugar and water dissolving, and paper shredding are a few examples of physical changes.
A liquid becomes a vapor when it is heated to its boiling point. When the vapor pressure of the liquid reaches atmospheric pressure, the state of the substance changes from liquid to gaseous. Since boiling is a physical process, molecules are unaffected.
When atoms or molecules spread apart enough during boiling to transform a liquid into a gaseous state, bubbles and steam are produced.
The point at which a liquid begins to boil is known as the boiling point. Water boils at 100oC at 1 atm of pressure. How quickly a liquid boils is influenced by the temperature, air pressure, and liquid vapor pressure. The liquid begins to boil when the air pressure and liquid vapor pressure are equal.
What is a Chemical Change?
A chemical reaction takes place when one or more substances, referred to as reactants, change into one or more unique substances, referred to as products. Chemical components and elements are examples of substances. A chemical reaction produces a variety of substances as products by rearranging the atoms that make up the reactants. Although there is the same number of atoms both before and after the chemical reaction, there are different numbers of molecules.
Is Boiling Water a Physical Change?
Yes, boiling water is a physical change.
Due to the fact that water’s chemical makeup remains constant during the boiling process, this is the case.
It is also possible to reverse the process. Recovering liquid water is as simple as cooling the vapors.

What Are Physical and Chemical Properties?
Physical properties are those that can be assessed without altering a substance’s chemical makeup.
For instance, it is possible to measure a substance’s size without affecting its chemical makeup.
Intensive and extensive physical properties are further divided into these categories.
Extensive properties are those whose value is altered by altering the mass of a substance, whereas intensive properties are those whose value is unaffected by altering the mass. Bulk properties include intensive properties.
For instance, when a substance’s mass changes, the substance’s volume also changes.
As a result, it is a large property. The temperature, on the other hand, is an intensive property that does not change as the mass does.
Chemical properties are those of a substance that cannot be measured without altering its chemical structure.
In order to study these, scientists typically look at how a substance reacts with other chemicals, air, water, acids, and bases. They investigate whether a chemical reaction can occur with the substance.
For instance, only when the resultant substance has a different composition can we study the reaction of hydrogen with a substance.
If the composition is the same, it follows that no chemical reaction has occurred.
Conclusion: A Physical Change
Since the chemical makeup of water does not change during boiling, there is no chemical change during boiling. Boiling only affects the physical properties. Boiling does not result in the formation of any new products.
FAQ
How hot does water get when it is specific?
The amount of heat needed to raise a substance’s temperature by one degree Celsius in one gram is referred to as its “specific heat.” The standard unit of measurement for specific heat is calories or joules per gram per degree Celsius. For instance, water has a specific heat of 1 calorie (or 4.186 joules) per gram per degree Celsius.
Without using heat, how can water be boiled?
Without the use of heat, water can be boiled. Since a liquid’s boiling point depends on its vapor pressure, ambient pressure, and temperature.
It is possible to lower water’s boiling point to room temperature by increasing the pressure on the water’s surface inside of a sealed, insulated vessel.
Why doesn’t boiling water’s temperature change?
Since all of the heat energy is used up in the process of converting water from liquid to gaseous water vapor, the temperature of the water doesn’t change while it is boiling.