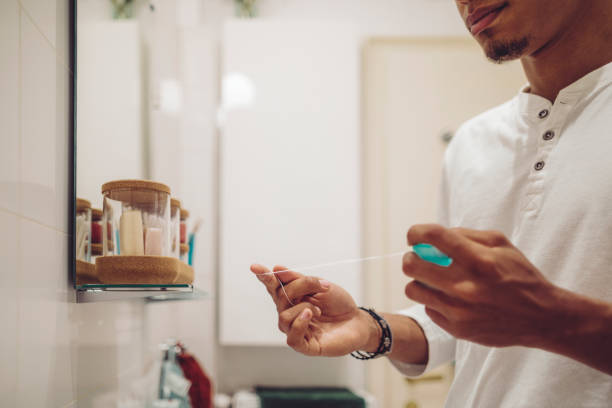
Do you still have a toothache after flossing? There are others who experience this, so don’t worry! Particularly for those who are performing it for the first time, this circumstance is fairly typical. However, there are cases where flossing ache is a sign of more serious tooth issues. To find out whether you need to schedule an appointment at a dental clinic, check out these common causes.
Table of Contents
Causes of Teeth Hurt After Flossing
New at Flossing
People who are novice flossers are more likely to experience pain after or during the procedure. Improper techniques and tools are the most common reasons for this unpleasant ache.
The end result of flossing is to remove potential bacterial breeding grounds by inserting a thin, sharp rope between your teeth. On the other hand, it shouldn’t hurt. Try using kinder, slower flossing motions rather than being angry.
After you change your approach, the pain should slowly go away. If it doesn’t, speak with your dental office to determine whether you are dealing with a more serious problem.
Tooth Decay
There is no doubt that brushing and flossing help to reduce the number of bacteria in our mouths. Bacteria unfortunately occasionally manage to evade their enemy. Decay, cavities, and infections develop when it accumulates. Therefore, tooth decay is the second cause of your painful floss.
There is only one place where the pain you are feeling could be. In this case, you probably have decay or cavities in that exact place. Wherever you normally floss, bacteria are known to collect in the corners and spaces between teeth.
Watch out for additional indications of tooth damage, such as pain when eating and sensitivity to temperature changes. Make a dental examination a priority right away if the pain persists or starts to worsen.
Sensitivity
For maintaining your oral health, flossing correctly is essential. But proper brushing is also important! When we do it too hard or when we use a strong toothbrush, our teeth can become more sensitive. Dentin hypersensitivity also referred to as tooth sensitivity, is a medical condition that manifests as a number of symptoms.
One of them is discomfort while flossing. Others include pain while drinking hot and cold beverages, discomfort while eating, and sensitivity to cold air. The dental office can quickly treat this condition.
It happens as a result of the enamel’s protective layer being damaged. When enamel wears off, more sensitive layers are exposed such as dentin. Because of the increased sensitivity of neural endings to environmental factors, we experience both mild and severe toothaches.
Gum Disease
Gum disease represents the worst-case scenario. Gingivitis is a condition with a medical name, and poor or nonexistent oral hygiene can lead to it. Other symptoms include bleeding, swollen gums, tenderness, redness and inflammation, and bad breath.
People with this condition who floss will undoubtedly feel pain. This is a result of the substantial amount of plaque and tartar that is being removed from their teeth. But don’t worry, brushing and flossing are the best things you can do to heal gingivitis.
Periodontitis will undoubtedly be avoided, though it may hurt initially. This is the last stage of gum disease which can result in severe situations such as tooth loss. You must speak with a dental expert to get gingivitis treated permanently.

Loose Dental Restorations
Do you have a history of extensive dental work? In that case, pain from flossing may be caused by things like loose dental restorations.
“Restorations” refers to things like crowns over your teeth. All crowns eventually require replacement because when they become loose, numerous nerves are exposed. Additionally, flossing with such exposed nerves can cause excruciating pain.
Even simple fillings will eventually crack, regardless of whether you have a crown. It can hurt just as much to floss when such fillings are cracked.
The only real solution for these problems is to see a dentist. You’ll feel as though you have a completely new mouth by the time you leave the session!
Issues With Braces and Retainers
Do you have braces or a retainer? In that case, there are instances where flossing can be painful.
For instance, it is normal to experience pain after flossing if you recently had your braces adjusted. In that case, your teeth likely hurt because of the adjustment and not because of the way you are flossing.
If you have a permanent retainer, the flossing technique is usually to blame. The simple truth is that flossing with a retainer is more difficult than flossing without one. With patience and practice, you can master the right techniques and make the pain go away entirely.
Rough Toothbrush
If you’re reading this, you probably want to know why your flossing technique is flawed. But did you know that the primary problem might be your toothbrush?
In general, a toothbrush with soft bristles will help you clean your teeth more thoroughly. Some of the problems we’ve already covered may result from using a hard-bristled toothbrush.
For example, using an uncomfortable toothbrush for too long can make your teeth painfully sensitive. Tooth decay and even gum disease can result from it if it doesn’t adequately clean your teeth.
How to Floss Properly
Many people wonder, “What causes pain in my teeth after flossing?” Their improper flossing technique is the cause of the problem.
Typically, people who experience pain during or after flossing are those who are new to it. Improper tools and techniques are the most common reasons for toothache when flossing. In the end, flossing merely inserts a thin, sharp thread between your teeth to scrape away food particles and sticky plaque.
Here’s how to floss properly to prevent toothaches or sore gums after flossing.
• Use a length of floss that is 18 inches long and wrap it around the middle fingers on both hands.
• With your thumbs and forefingers, tightly grasp the floss.
• Then, carefully place it in between the teeth.
• Curve the floss into a “C” shape against the side of the tooth.
• Maintaining pressure against your tooth, gently move the floss up and down.
• Also, floss under the gum line, but then again, do so gently and slowly to avoid gum bleeding or damage.
Note:
• Don’t snap or jerk the floss, as it can cause flossing pain.
• Floss between your back teeth every day.
• Don’t over-floss if your gums are inflamed.
Conclusion
Whatever the root of your toothache, keep flossing. Most often, the pain you experience is the result of your teeth becoming accustomed to being cleaned properly. This is crucial in the case of gingivitis. Periodontitis will develop if it is not properly treated in its early stages.
Always use gentle motions and talk to your dentist before doing anything. Ask any and all questions that come to mind without holding back. For the sake of your general well-being, oral hygiene and health are crucial.